How to Choose the Right PCB Feeder Machine?
Selecting an appropriate PCB feeder machine is a critical decision for electronics manufacturers aiming to optimize their Surface Mount Technology (SMT) production lines. A PCB feeder plays a vital role in automating the supply of components during assembly, directly impacting line efficiency, accuracy, and product quality. This article explores key considerations for choosing the right feeder machine, examines various types available in the market, and highlights the influence of supporting equipment, including SMT peripheral equipment, on overall system performance.
Understanding the Role of PCB Feeders
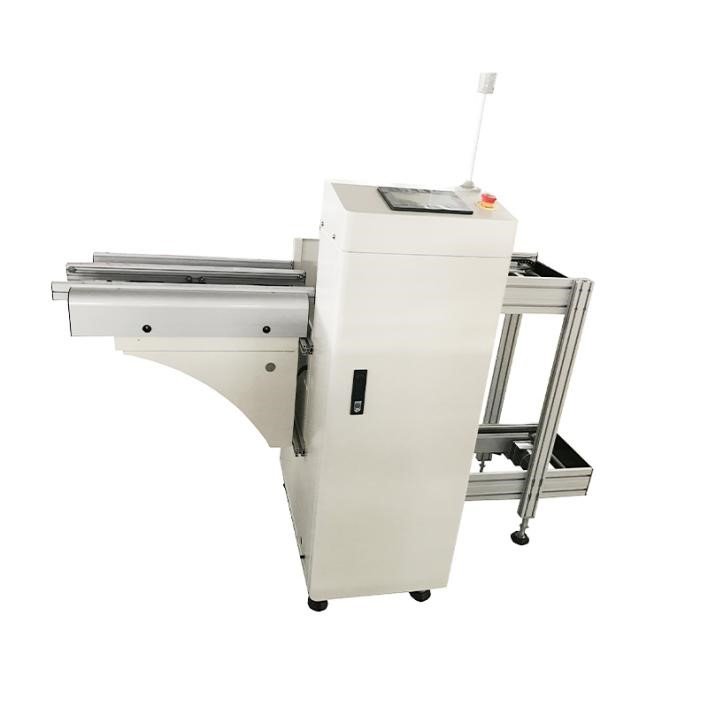
A PCB feeder machine is designed to deliver components precisely and consistently to pick-and-place machines during the SMT assembly process. By automating the component supply, feeders reduce manual labor and enhance production speed while ensuring components are presented in optimal orientation and timing. Given their importance, selecting the right feeder involves a thorough understanding of production needs and machine compatibility.
PCB feeders vary widely in design and functionality. The ideal choice depends on factors such as component types handled, production volume, feeder compatibility, and integration with existing equipment.
See also: How SEO Audit Services Can Boost Your Search Rankings?
Key Factors to Consider Before Selection
Component Compatibility and Range
Different feeders support varying component sizes and packaging formats, including tape-and-reel, tray, and tube. When selecting a PCB feeder, it’s essential to ensure that it can handle the types of components your assembly line uses. For example, tape feeders are prevalent for small resistors and capacitors, whereas tray feeders are better suited for larger or fragile parts.
Precision and Reliability
Accuracy in component delivery minimizes errors during placement, reducing waste and rework. The selected feeder should provide stable feeding without misalignment or jams. High-quality feeders feature mechanisms for precise indexing and tension control, which maintain consistent supply rates and reduce downtime.
Speed and Throughput Requirements
Production speed demands vary by manufacturing scale and product complexity. High-speed feeders support rapid component delivery essential for high-volume assembly lines. However, speed should never compromise accuracy; a balance between throughput and reliability is critical.
Integration and Compatibility
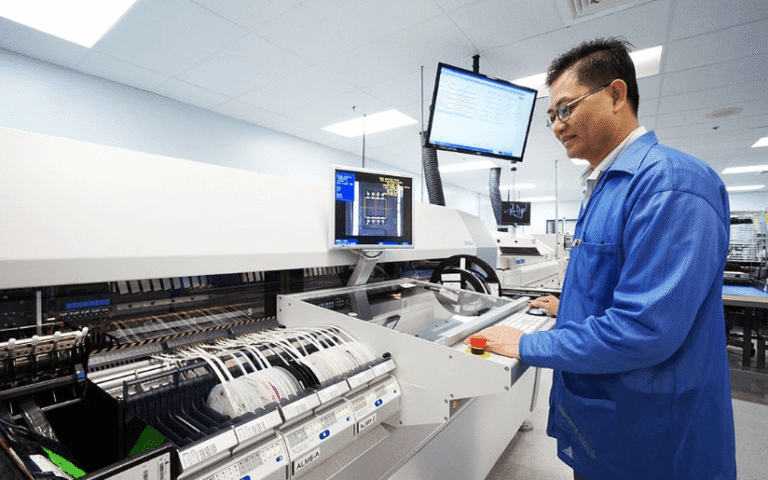
A feeder must integrate seamlessly with pick-and-place machines and other SMT peripheral equipment. Compatibility with control systems, communication protocols, and physical interfaces reduces installation challenges and facilitates smoother operations.
Maintenance and Support
Ease of maintenance impacts long-term productivity. Feeders with modular designs and accessible components simplify repairs and reduce machine downtime. Additionally, supplier support for parts and technical assistance should factor into the purchasing decision.
Types of PCB Feeder Machines
PCB feeders can be broadly classified based on feeding mechanisms and component packaging compatibility:
- Tape Feeders: These handle components packaged in tape and reel, providing continuous supply for small, uniform parts. They are standard in most SMT lines due to versatility and availability.
- Tray Feeders: Designed for larger or sensitive components housed in trays, these feeders use robotic pick mechanisms to present parts. They offer gentle handling but typically have lower speed compared to tape feeders.
- Tube Feeders: Less common, tube feeders supply components packaged in tubes, often used for unique or specialty parts.
Choosing the appropriate type depends on component characteristics and production priorities.

Enhancing Production with Supporting Equipment
A well-rounded SMT line includes more than just pick-and-place machines and feeders. SMT peripheral equipment, such as conveyors, loaders, and inspection stations, plays a crucial role in maintaining line balance and quality control. For instance, conveyors synchronize component feeding with placement speeds, preventing bottlenecks. Automated inspection tools detect feeder misfeeds early, minimizing defect propagation.
Investing in compatible and efficient peripheral equipment alongside the right PCB feeders ensures smooth workflow and maximizes throughput.
Challenges in Feeder Selection and Solutions
Choosing a PCB feeder is not without challenges. Common issues include:
- Feeder Jamming: Caused by poor tape quality or misaligned components; high-precision feeders with tension adjustment help mitigate this.
- Component Damage: Fragile parts require gentle feeding mechanisms, which tray feeders often provide.
- Changeover Time: Switching feeders for different components can consume valuable production time. Selecting feeders with quick-change features can enhance flexibility.
Addressing these challenges during the selection phase prevents costly disruptions later.
Practical Tips for Effective Decision-Making
- Conduct a thorough audit of the components to be handled, including size, weight, and packaging.
- Assess the existing SMT line’s compatibility with new feeders to avoid integration issues.
- Evaluate vendor reliability, including after-sales support and parts availability.
- Prioritize feeders that offer automation features such as self-calibration and error detection.
- Consider future production plans to ensure feeder scalability.
Conclusion
Selecting the right PCB feeder machine is essential for optimizing SMT assembly processes. A suitable feeder enhances component delivery accuracy, boosts line speed, and integrates seamlessly with pick-and-place systems and other SMT peripheral equipment. Careful consideration of component compatibility, machine reliability, speed requirements, and maintenance ease guides manufacturers toward the most fitting solution.
By addressing these factors strategically, electronics manufacturers can improve production efficiency, reduce downtime, and maintain high-quality standards in their SMT operations.